SD WAN
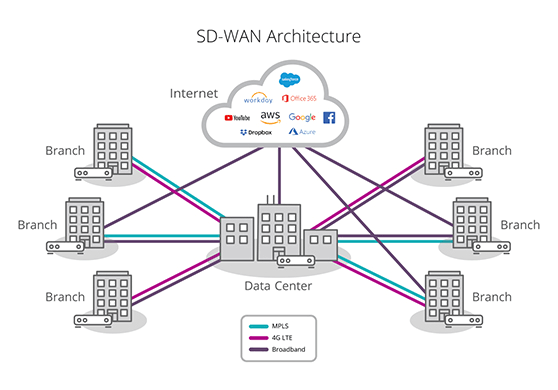
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) is a virtual WAN architecture that allows enterprises to leverage any combination of transport services—including MPLS, LTE and broadband internet services—to securely connect users to applications.
What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
The traditional WAN architecture was limited to enterprise, branch, and data center. Once an organization adopts cloud-based applications in the form of SaaS and IaaS, its WAN architecture experiences an explosion of traffic accessing applications distributed across the globe.
These changes have multiple implications for IT. Employee productivity may be compromised by SaaS-application performance problems. WAN expenses can rise with inefficient use of dedicated and backup circuits. IT fights a daily, complex battle of connecting multiple types of users with multiple types of devices to multiple cloud environments.
With SD-WAN, IT can deliver routing, threat protection, efficient offloading of expensive circuits, and simplification of WAN network management.
✅ Better Performance – Optimizes network traffic, reduces latency, jitter, and congestion.
✅ Higher Reliability – Automatic failover ensures network uptime during an outage.
✅ Lower Costs – Uses affordable broadband and LTE instead of expensive MPLS circuits.
✅ Stronger Security – Built-in firewalls, VPNs, encryption, and SASE (Secure Access Service Edge).
✅ Cloud & SaaS Optimization – Direct access to AWS, Microsoft 365, Zoom, Azure without backhauling traffic.

Some examples of SD-WAN use cases include
- Connecting major offices & HQs to each other, or central data-centres
- Connecting data-centres to each other
- Connecting branch sites to HQ or a data-centre
- Connecting smaller regional or international offices into the corporate network
- Connecting to the Internet, either via a central gateway, or with multiple connections into a number of sites
- Direct connections to public cloud or hosted services
- Direct connections to partners or industry-wide networks
- Remote access for home-workers and mobile users
- SD-WAN architecture: How SD-WAN works
SD-WAN vs. Traditional WAN (MPLS)
| Feature | Traditional WAN (MPLS, VPNs) | SD-WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Routing | Static, fixed paths | Dynamic, intelligent routing |
| Cloud Optimization | Requires backhaul through data centers | Direct-to-cloud connectivity |
| Failover Handling | Manual | Automatic failover |
| Security | Basic VPN & firewalls | Advanced security (SASE, Zero Trust) |
| Cost | Expensive | More affordable |
| Management | Requires on-site configuration | Centralized, cloud-based |